Water Based Exercise Can Be a Fun and Stimulating Experience for Stroke Patients
2023-01-12 - Swimming
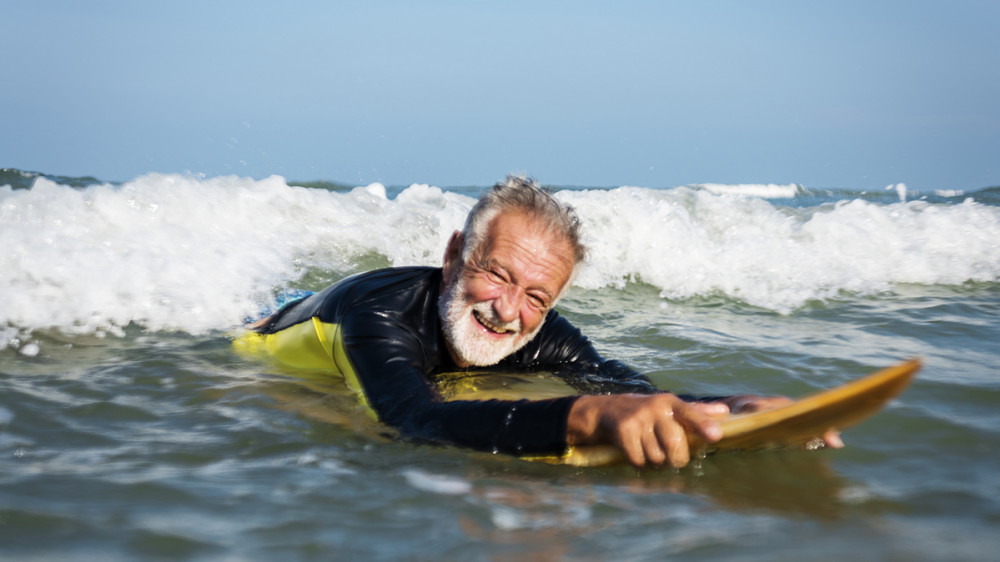
Swimming can be beneficial for stroke patients as it is a low-impact form of exercise that can help improve cardiovascular fitness, muscle strength, and range of motion. It also provides a sense of buoyancy that can make it easier for stroke patients to move their limbs. However, it is important for stroke patients to consult with their healthcare provider before starting any exercise program, including swimming, to ensure that it is safe and appropriate for their individual needs and condition.
When body is submerged in water, the natural buoyancy of water helps to reduce the body weight of patients. Moreover, the viscosity of water will provide resistance when our body moves in water. The body works harder to circulate blood due to the pressure that acts on the body. By swimming, patients get the benefits of a cardio workout as since the medium of exercise is water, body is protected from falls.
Hydrotherapy refers to the use of water for the treatment of various medical conditions. This can include things like using warm water to relax muscles and reduce pain or using cold water to reduce inflammation. Hydrotherapy can be done in a variety of settings, including swimming pools, hot tubs, and showers.
Aquatic therapy, on the other hand, refers specifically to the use of water-based exercises and activities to help people recover from injuries or illnesses. It is typically performed in a pool and led by a physical therapist or other healthcare professional. Aquatic therapy can include exercises such as walking, jogging, or cycling, as well as stretching and resistance training.
So, in short, aquatic therapy is a type of hydrotherapy that involves exercise in water.
The buoyancy and resistance provided by the water can help to reduce stress on joints and muscles, making it an effective treatment for a wide range of conditions, including arthritis, chronic pain, and injuries. Aquatic therapy may be used as part of a rehabilitation program following an injury or surgery, or as a way to manage chronic conditions. Aquatic therapy is typically led by a physical therapist or other healthcare professional.
Swimming can be considered a form of aquatic therapy. The buoyancy and resistance of the water can help to reduce stress on joints and muscles, making it an effective exercise for many people. It can be used to improve cardiovascular fitness, strength, and flexibility. Swimming is a low-impact exercise, which makes it a good option for people with certain conditions, such as arthritis, that can be made worse by high-impact activities.
Swimming as aquatic therapy is often used as part of a rehabilitation program following an injury or surgery, or as a way to manage chronic conditions. People with pain or disabilities that make land-based exercise difficult may also benefit from swimming as aquatic therapy. It is typically led by a physical therapist or other healthcare professional, who will develop an individualized swimming program tailored to meet the patient's specific needs and goals.
Some of the benefits of aquatic therapy for stroke patients include:
Strength - When we move in water, natural resistance is provided by it and this will contribute to gaining more strength in lesser time. Therefore, exercising in water is liking getting a strength workout from each session we attend. It is a good form of exercise or those who find it difficult to perform on land surface. A person who has weak legs will be able to do squats and lunges in water., They are more at ease when working out in water and this sometimes enables them to regain their lost capabilities like walking.
Pain Reliever – Water acts as the best form of pain reliever. The pressure of water will offer effective massages on muscles, that will help to reduce the pain after each session. This effect is more pronounced if the water is warm and usually around body temperature. Warm water stimulates the release of endorphins and reduces tension in the body. Endorphins are body’s natural pain killers.
Cardiovascular Health: Cardiovascular fitness can be increased in a low impact way by submerging in water. By simply standing in water, the increased pressure on the body forces the heart to work harder to move blood, increasing the heart’s fitness over time. Cardiovascular health not only helps increase a stroke patient’s endurance, but it can also help reduce the risk of the patient experiencing another stroke.
Improved Mobility: Stroke patients can move easily in water without placing stress on their joints as submerging in water decreases their body weight by 90 percent. And, the water’s viscosity means that a person moves more slowly through it. Therefore, water will provide extra support for the body, allowing a stroke patient to work on balance and coordination more freely. These two aspects of water combined provides an excellent therapy environment for stroke paralysis. Even if patients are not strong enough to complete these exercises on land, they can work on range-of-motion exercises and simulated walking in the water, and they can get extra support from flotation devices whenever necessary.
Muscle Relaxation: A common issue faced by stroke patients is muscle spasticity. Muscle spasticity results in stiff or rigid muscles that turns painful with time. Hydrotherapy, especially in a warm pool has been found to relax these muscles, reducing spastic episodes. It thus allows the patient and their therapist to work toward lengthening the muscle.
Balance Training: Strokes tend to affect one side of the body over another and therefore stroke patients often tend to have issues with their balance, making it difficult to walk or perform daily activities. Aquatic therapy can help with this, providing a safe environment for balance training. Hydrotherapy, in fact, is often more effective than land-based training in this area, since water protects the patient from falling as they work through their exercises. The patient can be progressed by adding water disturbances manually or with a resistance jet to increase the difficulty.
Working out in the water can be a fun and stimulating experience for stroke patients, especially in group settings. Not only do the patients get a good exercise in the water, but they also affect their emotional well-being by gaining a sense of progress and independence. All these factors combined help make the road to recovery much smoother.
Hydrotherapy Exercises for Stroke Patients:
Some examples of hydrotherapy exercises that may be used for stroke patients:
Walking or jogging in the water: This can help to improve balance and coordination, as well as cardiovascular fitness.
Arm and leg exercises: Stroke patients may have difficulty with movement on one side of their body. Hydrotherapy exercises that focus on the affected limb can help to improve strength and range of motion.
Resistance exercises: Using equipment such as pool noodles or resistance bands can help to increase muscle strength and endurance.
Stretching: Gentle stretching exercises in the water can help to improve flexibility and reduce muscle stiffness.
Breathing exercises: Hydrotherapy can also be used to help stroke patients with respiratory issues. Exercises such as blowing bubbles or blowing up a ball can help to improve lung function.
It is important to note that stroke patients should be evaluated by a physical therapist and a physician before starting an aquatic therapy program. The intensity and frequency of the exercises will depend on the individual's condition and capabilities.
Swimming can be a beneficial form of exercise for stroke patients, but it is important that they do not have a fear of water and are comfortable in the pool. A physical therapist or doctor should be consulted before starting a swimming program to ensure it is safe and appropriate for the individual's condition.
.







.jpg)